Let’s consider elliptic problem (*) on the cube 0≤x≤1, 0≤y≤1, 0≤z≤1, with Laplace operator
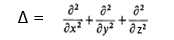
Similar to 2-dimensional problem we set boundary conditions on the faces of the cube
u(0, y) = u(1, y) = u(x, 0) = u(x, 1) = 0, 0≤x≤1, 0≤y≤1.
Furthermore, we subdivide cube on n3 equal small cubes and apply finite differences schema for axis x, y и z with h = 1/n.
After that, as in 2-dimensional case, we reorder indexes of vector u (to receive a vector indexed with by index) and, as a result, we obtain a system of linear equations with the matrix that looks like this:
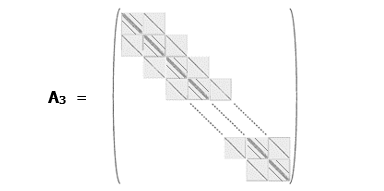
This matrix has dimensions N х N, where N = (n + 1)3.
On its main diagonal, we have 3-diagonal blocks of the size (n + 1)2 similar to matrix А2 from 2-dimensional problem – we just need to replace all numbers 4 to number 6 (i.e. on the main diagonal of these blocks we must put 6 + σj instead of 4 + σj as it was in 2-dimensional problem).
The blocks above and below these diagonal blocks are the diagonal blocks of the size (n + 1)2 with -1 on the main diagonal.
Thus, 3-dimensional problem differ not too much from 2-dimensional problem (and for our solver the problem is practically the same).
